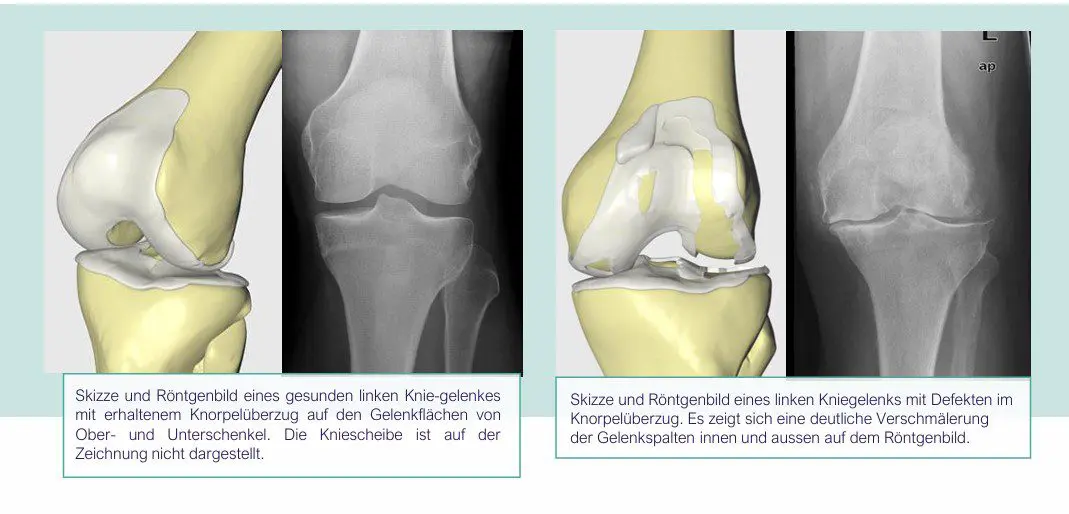
Wear and tear of the knee joint is known as osteoarthritis. This is a wear and tear of the cartilage lining, often accompanied by inflammatory processes.
Cause of knee osteoarthritis
The causes of knee osteoarthritis can be age-related or due to malalignment (e.g. bow legs, knock-knees). Earlier injuries such as a torn cruciate ligament or meniscus, operations or diseases such as rheumatism also frequently lead to the development of osteoarthritis.
Typical symptoms of knee osteoarthritis
As it progresses, the wear and tear causes pain in and around the knee. These usually occur after prolonged sitting or after exertion, such as prolonged walking. Climbing stairs in particular is often painful. Inflammation can also cause pain at rest and at night. It can also lead to restricted movement and instability.
Diagnosis of knee osteoarthritis
The course of the disease, the clinical examination and an X-ray are decisive for the diagnosis of osteoarthritis. X-rays show cartilage wear due to the narrowing of the joint space. The images are taken with the joint under load in a standing position, and the entire leg axis is also examined. If necessary, "stress images" can be taken to assess ligament stability and the condition of the knee.
An MRI scan is useful for specific questions about cartilage, menisci or ligaments, but is rarely necessary to clarify osteoarthritis.